해시
.#1
from collections import Counter
def solution(participant, completion):
part_counter = Counter(participant)
comp_counter = Counter(completion)
# 차집합으로 남은 한 명 찾기
answer = part_counter - comp_counter
return list(answer.keys())[0]- Counter 는 리스트 안의 각 요소가 몇 번 등장했는가 세는거
- Counter 함수 : 들어오는 리스트 안의 각 요소에 대한 갯수를 세겠다
- ex. ["leo", "kiki", "eden"] → Counter({'leo': 1, 'kiki': 1, 'eden': 1})
- answer 변수 : 참가자 - 완료한 애 > 미완료자 찾겠다
- return list(answer.keys())
#2
def solution(nums):
# 중복 제거하여 폰켓몬 종류 수를 셈
kinds = len(set(nums))
# 선택할 수 있는 총 마릿수는 전체 절반
max_pick = len(nums) // 2
# 다양한 종류를 최대한 고르기 위해, 위 둘 중 작은 값이 최대 종류 수
return min(kinds, max_pick)- set() : 중복 제거 함수
- len() : 길이 세는 함수
- // 는 : 정수 나눗셈
- min() : 두 개 중에 더 작은 값 고르겠다
#3 전화번호 목록
def solution(phone_book):
# 1. 전화번호를 정렬합니다. (접두어가 앞쪽에 오도록)
phone_book.sort()
# 2. 인접한 두 전화번호만 비교
for i in range(len(phone_book) - 1):
# 3. 다음 번호가 현재 번호로 시작한다면 접두어 관계가 있음
if phone_book[i+1].startswith(phone_book[i]):
return False
# 4. 접두어가 하나도 없으면 True 반환
return True- .sort() 사전순으로 정렬, ex. 123,124215,99202323 이런식으로
X
#4
from collections import defaultdict
def solution(clothes):
clothes_dict = defaultdict(int)
# 의상 종류별 개수 세기
for name, type_ in clothes:
clothes_dict[type_] += 1
# 각 의상 종류별 (선택 + 안입는 경우) 곱하기
answer = 1
for count in clothes_dict.values():
answer *= (count + 1)
# 아무것도 안 입는 경우 하나 제외
return answer - 1- from collections import defaultdict : 딕셔너리 초기값 모두 0으로 만들겠다
#5 베스트 앨범
from collections import defaultdict
def solution(genres, plays):
genre_to_songs = defaultdict(list)
for i, (g, p) in enumerate(zip(genres, plays)):
genre_to_songs[g].append((p, i))
# 장르별 총 재생 수를 기준으로 정렬된 리스트
sorted_genres = sorted(genre_to_songs, key=lambda g: sum(p for p, _ in genre_to_songs[g]), reverse=True)
answer = []
for genre in sorted_genres:
songs = sorted(genre_to_songs[genre], key=lambda x: (-x[0], x[1]))[:2]
answer.extend(song_id for _, song_id in songs)
return answer- def solution(genres, plays): 장르( 리스트 형태 ) 랑 plays, 재생횟수 입력 받겠다
- genre_to_songs = defaultdict(list) : 장르별로 재생수, 고유번호 쌍들을 저장할 딕셔너리 만들겠다.
- list는 [] 같음, defaultdict(list)는 키가 없을 대 자동으로 [ ] 만들어주는 딕셔너리
정렬
#6 K번째 수
def solution(array, commands):
answer = []
for i, j, k in commands:
sliced = array[i-1:j]
sliced.sort() #정렬해주고
answer.append(sliced[k-1])
return answer- [i-1:j] 슬라이싱에서 0인덱스 시작이므로 -1 해줘야함
#7 가장 큰 수
def solution(numbers):
# 1. 모든 숫자를 문자열로 변환
numbers = list(map(str, numbers))
# 2. 정렬 기준을 커스터마이징: (x+y) > (y+x) 인 경우 x가 먼저 오게
numbers.sort(key=lambda x: x*3, reverse=True)
# 3. 정렬된 숫자들을 이어붙이기
result = ''.join(numbers)
# 4. 예외 처리: '0000...'이면 '0'으로
return '0' if result[0] == '0' else result
곱하기 3 해주는
#8 H-index
def solution(citations):
# 인용 횟수 내림차순 정렬
citations.sort(reverse=True)
# i는 0부터 시작 (논문 순서), c는 인용 횟수
for i, c in enumerate(citations):
# 현재 인용 수가 i+1보다 작으면, 그게 h-index 기준점
if c < i + 1:
return i
return len(citations) # 모든 논문이 i+1번 이상 인용된 경우- citiations 라는 array를 내림차순해준다. ctiations.sort(reverse=True)
- enumerate는 인덱스 값이랑 value 값을 추출해주는 함수, for i, c in enumerate(citiations):
완전탐색
#9 최소직사각형
def solution(sizes):
rotated = [(max(w,h), min(w,h)) for w, h in sizes]
max_w = max(w for w, h in rotated)
max_h = max(h for w, h in rotated)
return max_w * max_h
#10 모의고사
def solution(answers):
p1=[1,2,3,4,5]
p2=[2,1,2,3,2,4,2,5]
p3=[3,3,1,1,2,2,4,4,5,5]
score = [0,0,0]
for i, ans in enumerate(answers):
if ans == p1[i % len(p1)]:
score[0] += 1
if ans == p2[i % len(p2)]:
score[1] += 1
if ans == p3[i % len(p3)]:
score[2] += 1
max_score = max(score)
result = [i + 1 for i, s in enumerate(score) if s == max_score]
return result- result = [i+1 for i, s in enumerate(score) if s == max_score]
#11 소수 찾기
from itertools import permutations
def is_prime(n):
if n < 2:
return False
for i in range(2, int(n**0.5) + 1):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True
def solution(numbers):
nums = set()
# 1자리부터 전체 길이까지 모든 순열 생성
for r in range(1, len(numbers) + 1):
for p in permutations(numbers, r):
num = int(''.join(p))
nums.add(num) # 중복 제거 위해 set 사용
# 소수 판별 후 개수 세기
count = 0
for n in nums:
if is_prime(n):
count += 1
return count- from itertools import permutations : permutations 함수는 자리 바꿈, 순열을 만들어주는 함수
- def is_prime(n): 소수인지 판별하는 함수
#12 카펫
def solution(brown, yellow):
total = brown + yellow
for height in range(3, int(total ** 0.5) + 1)
if total % height == 0:
width = total // height
if (width - 2) * (height - 2) == yellow: #노란색 갯수 맞는지 체크
return [width, height]
- 7 // 2 = 3
#13 피로도
from itertools import permutations
def solution(k, dungeons):
max_count = 0
# 던전 순서의 모든 경우의 수를 순열로 생성
for perm in permutations(dungeons):
fatigue = k # 현재 피로도
count = 0 # 탐험한 던전 수
for min_req, cost in perm:
if fatigue >= min_req:
fatigue -= cost
count += 1
else:
break # 이 순열에서는 더 이상 탐험 불가
max_count = max(max_count, count)
return max_count- from itertools import permutations : 받은 array의 가능한 모든 순열만들 때
#14 전략망을 툴로 나누기
#15 모음사전
깊이/너비 우선 탐색( DFS/BFS )
#16 타겟 넘버
from itertools import product
def solution(numbers, target):
l = [(x, -x) for x in numbers]
s = list(map(sum, product(*l)))
return s.count(target)- from itertools import product 모든 가능한 데카르트 곱 생성시 사용, 여러 리스트를 받아서 가능한 모든 조합을 만들어줌
Reference
(1)

Reference
(2)
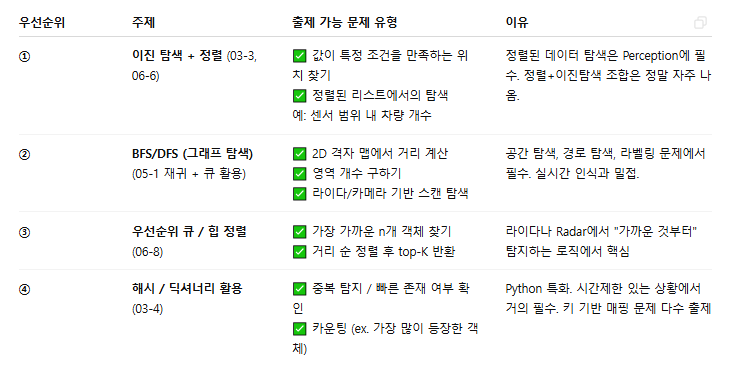
- 이진탐색 → bisect 모듈
- 우선순위 큐 → heapq 사용
- 해시 → dict, collections.Counter
- BFS → collections.deque
Reference based
#R1 정렬+이진탐색
distances = [10, 3, 7, 1, 6, 20, 15]
threshold = 7
import bisect
def solution(distances, threshold):
distances.sort()
return bisect.bisect_right(distances, threshold)
print(solution(distances, threshold))
#R2 해시( 딕셔너리 )
detections = ['car', 'person', 'car', 'bicycle', 'car', 'person']
counter = {}
def solution(detections):
for obj in detections:
if obj in counter:
counter[obj] +=1
else:
counter[obj] = 1
return max(counter.values())
print(solution(detections))- return max(counter.values())
#R3 우선순위 큐/heapq
(1) heapq 사용
distances = [12, 5, 3, 10, 7, 15, 1]
import heapq
def solution(distances,k=3):
return heapq.nsmallest(k, distances)
print(solution(distances))
(2) 일반 정렬 사용
distances = [12, 5, 3, 10, 7, 15, 1]
def solution(distances):
return sorted(distances)[:3]
print(solution(distances))
#R4 BFS/DFS, 너비우선탐색/깊이우선탐색
알고리즘 기초
#17 세 정수의 최댓값 구하기
a = int(input("정수 a의 값을 입력 : "))
b = int(input("정수 b의 값을 입력 : "))
c = int(input("정수 c의 값을 입력 : "))
maximum = a
if b > maximum: maximum = b
if c > maximum: maximum = c
print(f"최댓값은 {maximum} 입니다.")
#18 세 정수 받아서 중앙값 구하기
(1)
a = int(input("a입력"))
b = int(input("b입력"))
c = int(input("c입력"))
def me3(a,b,c):
if (b >= a and b <= c) or (b >= c and b <= a):
return b
elif (c >= a and c <= b) or (c >= b and a >= c):
return c
else:
return a
print(me3(a,b,c))
(2) sorted([a,b,c])[1] 사용
a = int(input("a입력"))
b = int(input("b입력"))
c = int(input("c입력"))
def me3(a,b,c):
return sorted([a,b,c])[1]
print(me3(a,b,c))
#19 1부터 n까지 정수의 합 구하기
(1) while 사용
n = int(input("n값을 입력하세요"))
sum = 0
i = 1
while i <= n:
sum += i
i += 1
print(sum)
(2) range 사용
n = int(input("n 값을 입력해라"))
sum = 0
for i in range(n)
sum += i+1
print(sum)
#20 a부터 b까지의 정수 합 구하기
a = int(input("a 값을 입력해라"))
b = int(input("b 값을 입력해라"))
sum = 0
for i in range(a, b+1):
sum += i
print(sum)
#21 +,= 번갈아 출력하기
a = int(input("a 값을 입력해라"))
for i in range(a//2):
print("+=",end='')
for j in range(a%2):
print('+',end='')
#22 직사각형 넓이로 변의 길이 구하기 47pg
area = int(input("직사각형의 넓이를 입력하세요 : "))
for i in range(1, area + 1):
if i * i > area: b
if area % i: continue
#23 1~12까지 8은 건너뛰고 출력
for i in range(1,13):
if i == 8:
continue
print(i, end=' ')
#24 왼쪽 아래가 직각인 이등변 삼각형으로 * 출력하기
n = int(input("n 값을 입력하세요 : "))
for i in range(n):
print('*' * (i+1))
#25 오른쪽 아래가 직각인 이등변 삼각형으로 * 출력하기
n = int(input("n 값을 입력하세요 : "))
print('')
for i in range(n):
print(' ' * (n-(i+1)),end='')
print('*' * (i+1))
이진검색
#26 bisect 모듈 사용 문제
arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13]
target = 5
import bisect
def solution(arr,target):
idx = bisect.bisect_left(arr,target)
if idx < len(arr) and arr[idx] == target:
return "YES"
else:
return "NO"
print(solution(arr, target))
'**Autonomous driving tech. > *Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Autonomous Car-자율주행차에서 인지기술이란? (0) | 2025.05.06 |
|---|---|
| Autonomous Car-카메라,레이더,라이다 센서 (0) | 2025.05.05 |
| Parameter Sharing(CNN), Rolling Shutter (0) | 2025.03.25 |
| [C++] 03.16 review Functor (0) | 2025.03.16 |
| 자율주행을 위한 인공지능 01 (0) | 2025.03.03 |